
Tutorial
Circulating cell-free DNA-based epigenetic assays involved in cfDNA methylation (5mC) [Nature 2018, PMID: 30429608], cfDNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC), [Cell research 2017, PMID: 28925386] and cfDNA nucleosome positioning (NP) [Nature Genetics 2016, PMID: 27571261], which were shown to be valid strategies for detecting various diseases, especially cancer. CFEA data portal integrating the human cell-free epigenomes of individuals with various conditions including health and disease states. The current release of CFEA contains the cell-free epigenomes of 1645 individuals involved in more than 80 billion raw sequencing reads. In order to keep the data processed and stored in a consistent manner, CFEA developed benchmarking pipelines aiming at a broad range of experimental methods to efficiently process handpicked datasets from raw files. CFEA provides easy-to-use and intuitive web interfaces and manuals for users to browse and obtain interesting data. The CFEA could be a valuable resource for accelerating the discovery and validation of liquid biopsy biomarkers to improve the diagnosis and outcomes of patients with complex diseases.
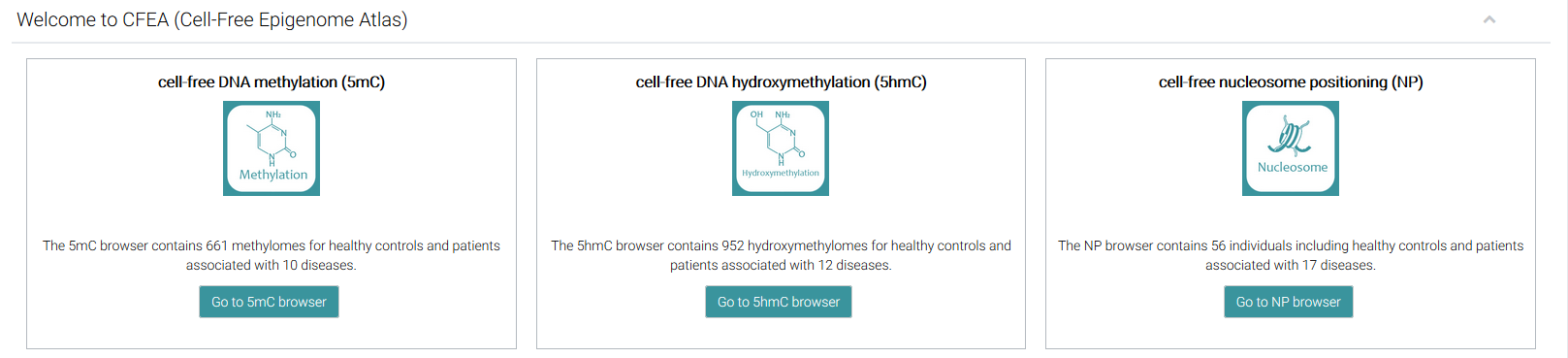
The home page contains 3 modification-specific browsers for users to easily browse and obtain different levels (DNA methylation [5mC], DNA hydroxymethylation [5hmC], and nucleosome positioning [NP]) of epigenetic data for cell-free DNA, the user can click the hyperlink embedded in the figure.
For example, after clicking the 'Go to 5mC browser' link, CFEA will open the "DNA methylation browser (5mC)" page.
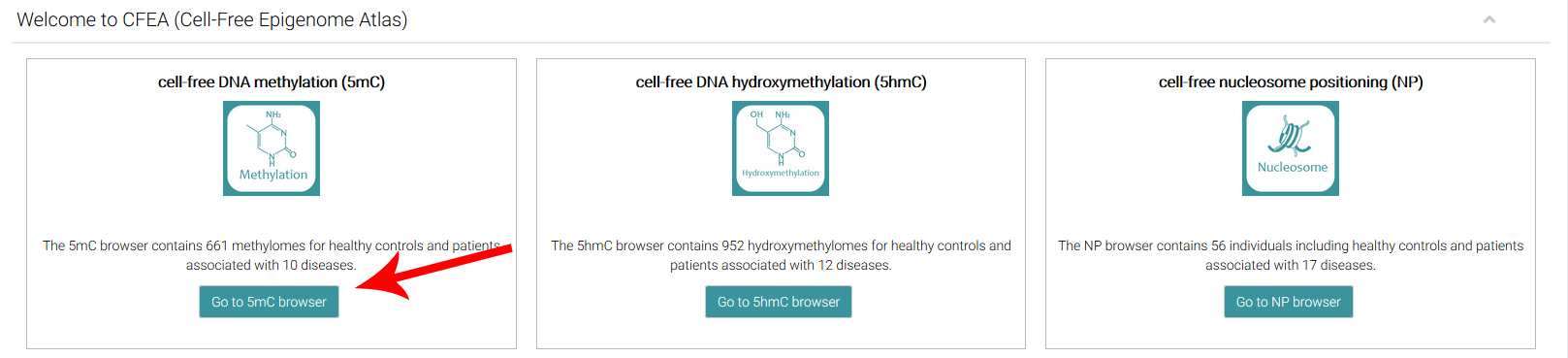
Several options were provided for users to easily compare epigenetic alterations in/near certain gene or genomic regions, and perform the comparison between samples (e.g., disease vs. health, cfDNA vs matched gDNA).
(1) Choose a disease you are interested in.
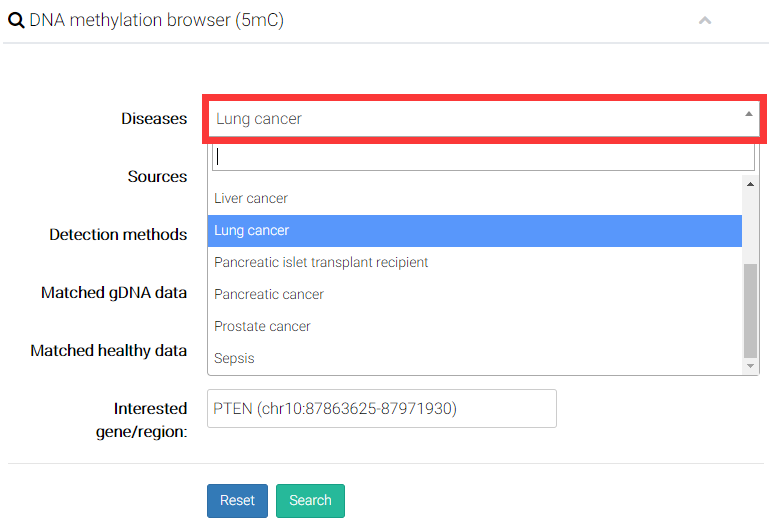
(2) Select the source of cell-free DNA. All the samples collected by CFEA were related to two components (plasma and serum) of blood.
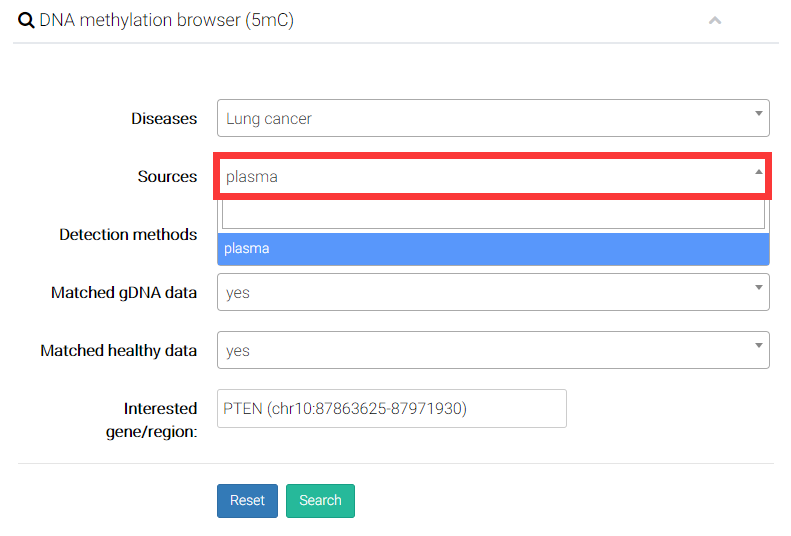
(3) Select a detection method.
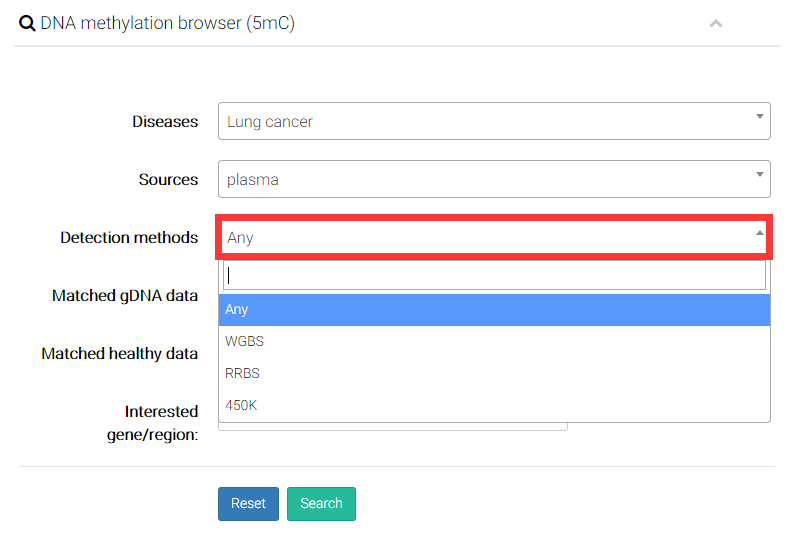
(4) Users can decide whether to display the genomic DNA (gDNA) samples from solid tissue with the same disease type of cfDNA samples.
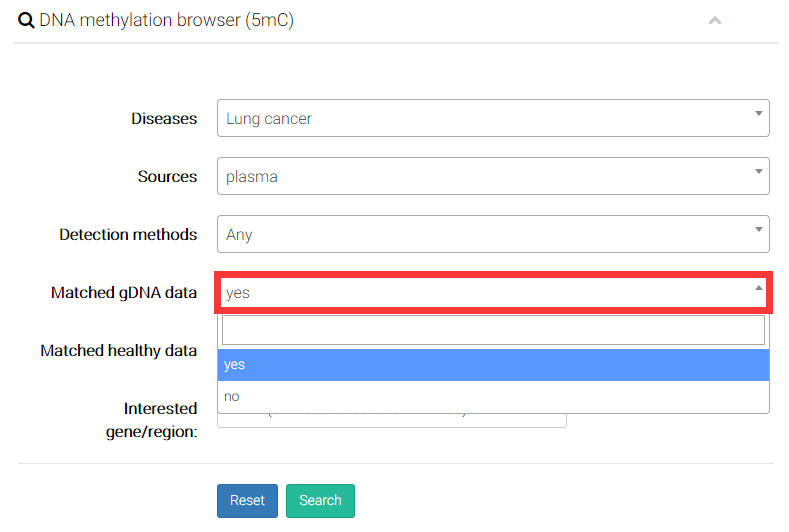
(5) Users can decide whether additionally display the genomic DNA (gDNA) samples from solid tissue with same disease type of cfDNA samples.
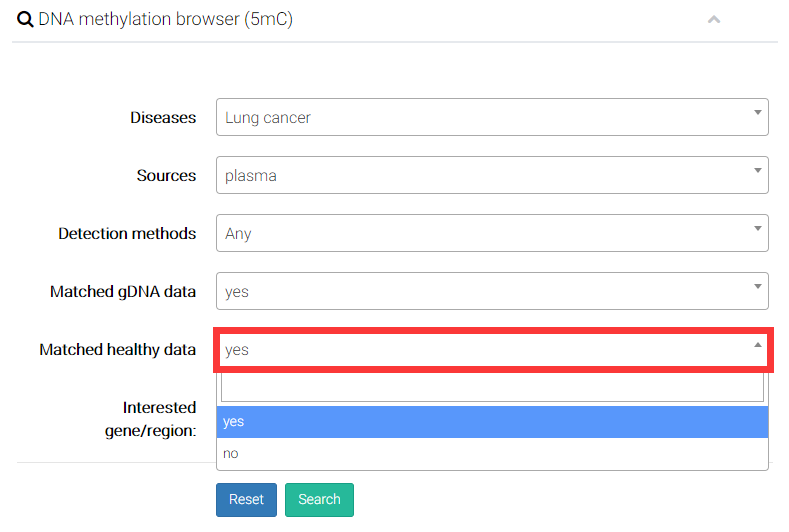
(6) Finally, User can input interested genes (e.g. PTEN) or particular genomic region (e.g. chr10:89596861-89754867), and directly compare epigenetic alterations in/near certain gene or genomic regions
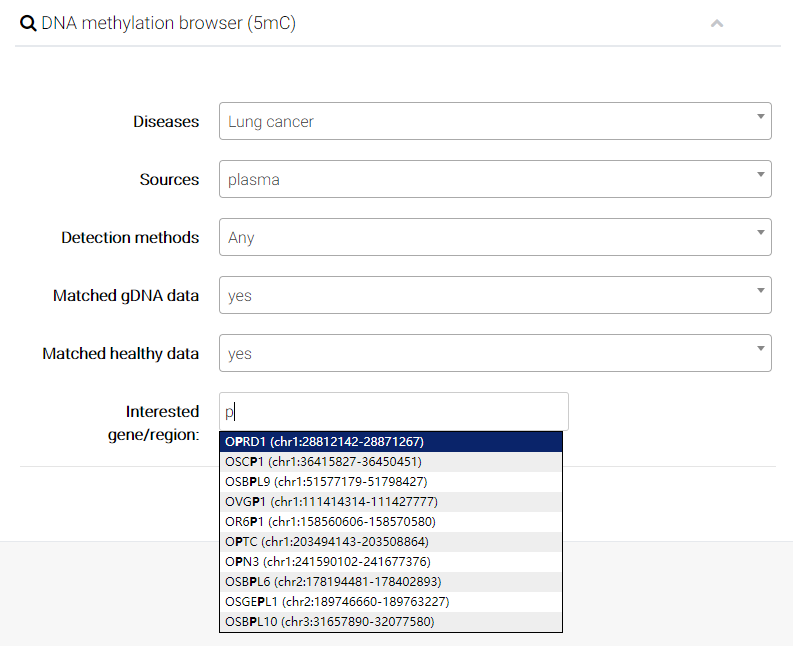
We also provide a detailed annotation for the four options at the right panel of the browser page.
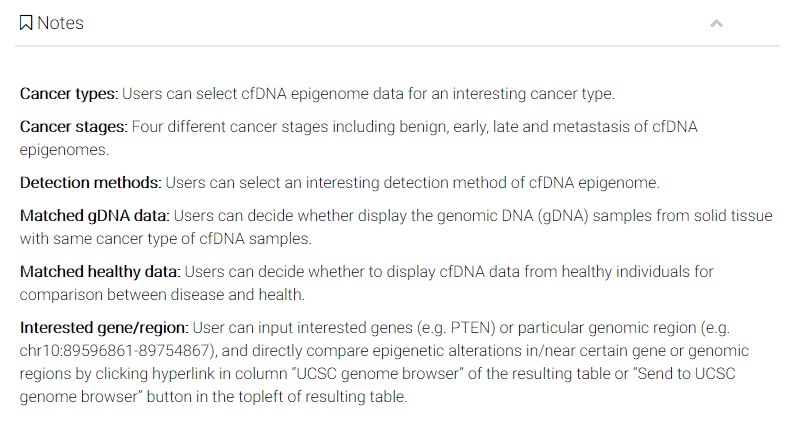
The corresponding entries will be shown in a brief table.
Table description: Each entry has 11 basic items.
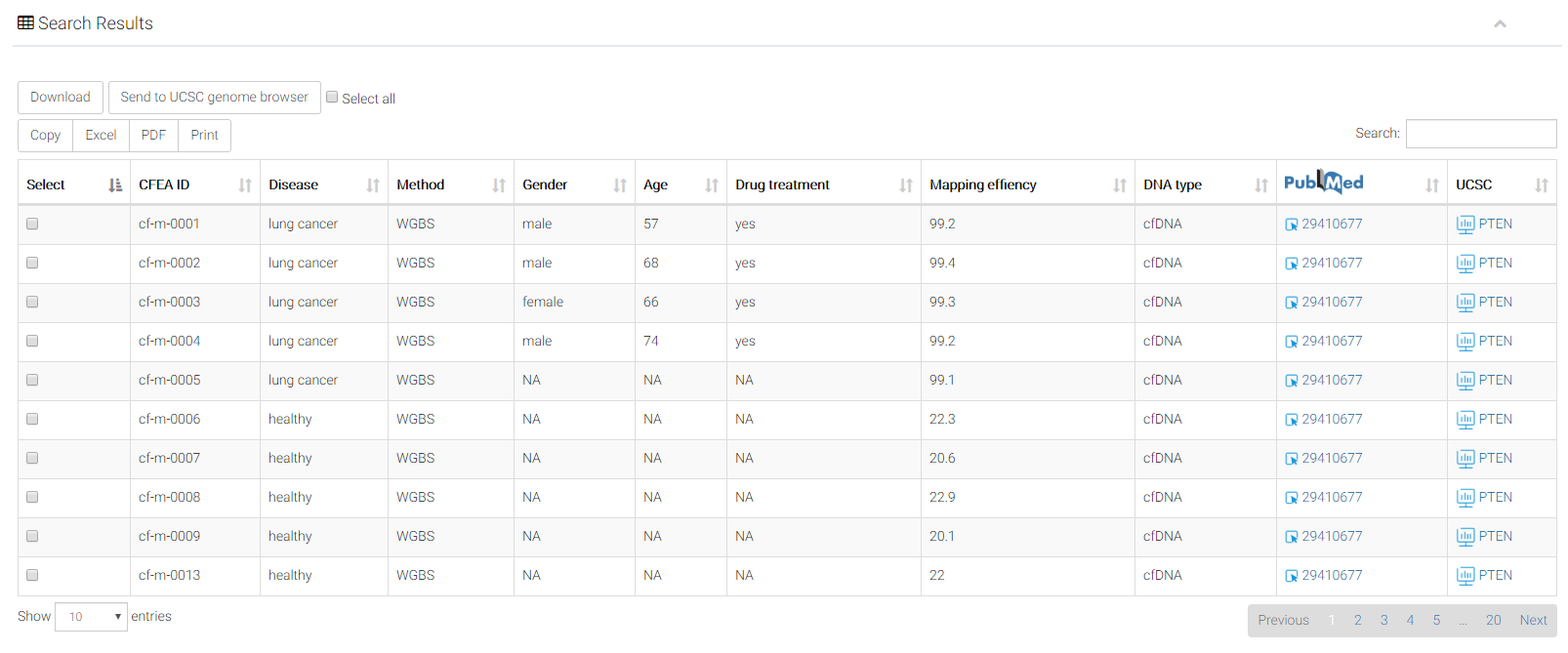
Select: you can select multiple samples simultaneously. Users can select all the samples by clicking "select all" button. By clicking the buttons "Download" or "Send to UCSC", you can further download or visualization the interested samples, respectively. Users can also export the table by clicking buttons including "copy" or "excel".
CFEA ID: Prefixes "cf-m", "cf-h" and "cf-n" represent samples detected with molecular levels of (5mC), cfDNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC), and cfDNA nucleosome positioning, respectively. Prefixes "gd-m", "gd-h" and "gd-n" represent those corresponding modifications of genomic DNA from disease-matched solid tissues.
Diseases: samples with different diseases.
Method: detection method.
gender: original annotation of sample gender.
age: original annotation of sample age.
Drug treatment: If the sample was treated by any drug before profiling.
Mapping effiency: as an important quality control measurment, the ratio of reads successfully mapped to reference genome was shown.
DNA type: this indicates the DNA type (either cfDNA or gDNA [genomic DNA]) of the epigenomic sample.
Pubmed: The original paper for this sample in the NCBI Pubmed database.
UCSC: you can click the button to visualize the bigwig file of this sample in the UCSC genome browser.
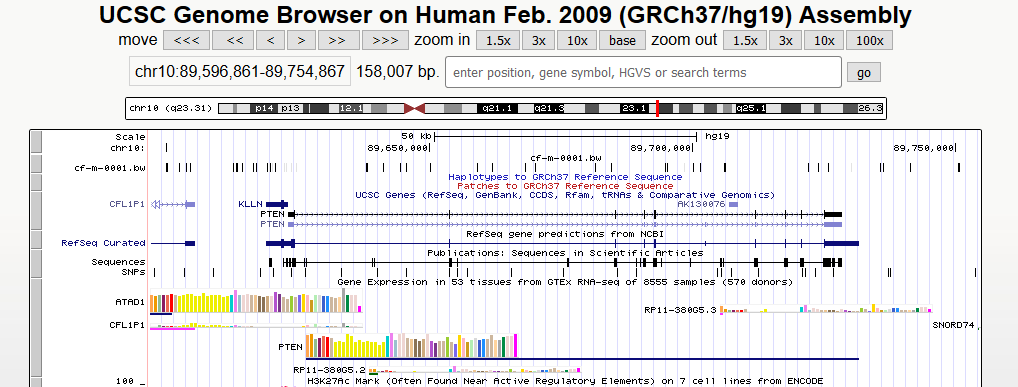
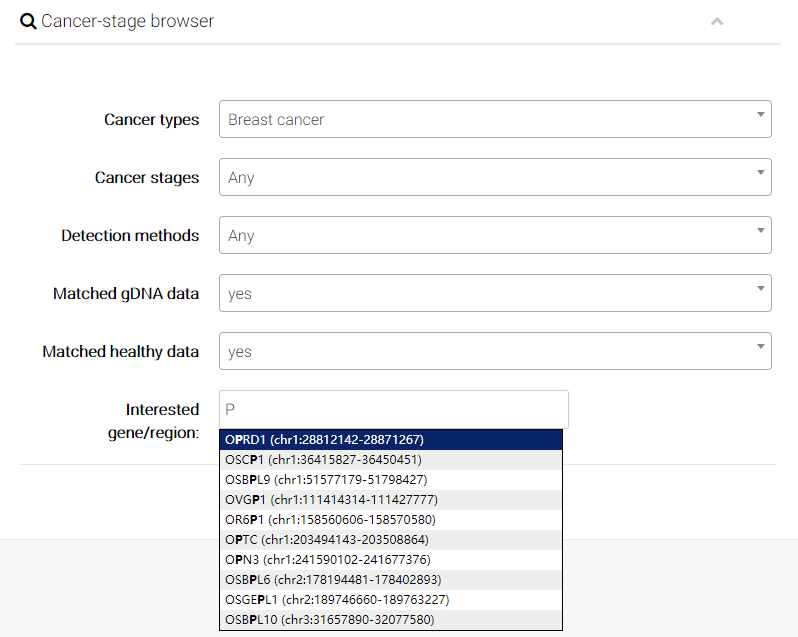
In recent years, circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has gained increasing attention as a noninvasive alternative to tissue biopsies and potential surrogate for the entire tumor genome. Accumulating evidence reveals large-scale epigenetic alterations of cfDNA exhibit high performance of sensitivity and specificity in the detection and classification of cancers. We thus collected the detailed metadata of CFEA samples from the original papers and developed cancer-specific browser to facilitate cancer-specific liquid biopsy-based biomarker discovery. Overall, the usage of cancer-stage browser is similar to sub-browser as mentioned above.
(1) Choose a cancer type you interested.
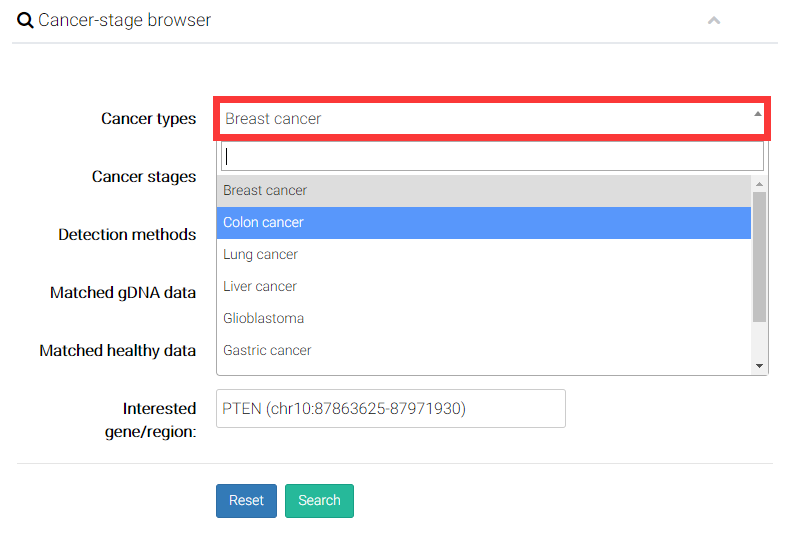
(2) User can choose an interesting cancer stage. There are 4 different clinical tumor stages including benign tumor, early-stage malignant tumor, late-stage malignant tumor, and malignant tumor with metastasis.
(3) Select a detection method (molecular levels of epigentic modifications).
(4) Users can decide whether to display the genomic DNA (gDNA) samples from solid tissue with the same cancer type of cfDNA samples.
(5) Users can decide whether additionally display the genomic DNA (gDNA) samples from solid tissue with same cancer type of cfDNA samples.
(6) Finally, User can input interested genes (e.g. PTEN) or particular genomic region (e.g. chr10:89596861-89754867), and directly compare epigenetic alterations in/near certain gene or genomic regions.
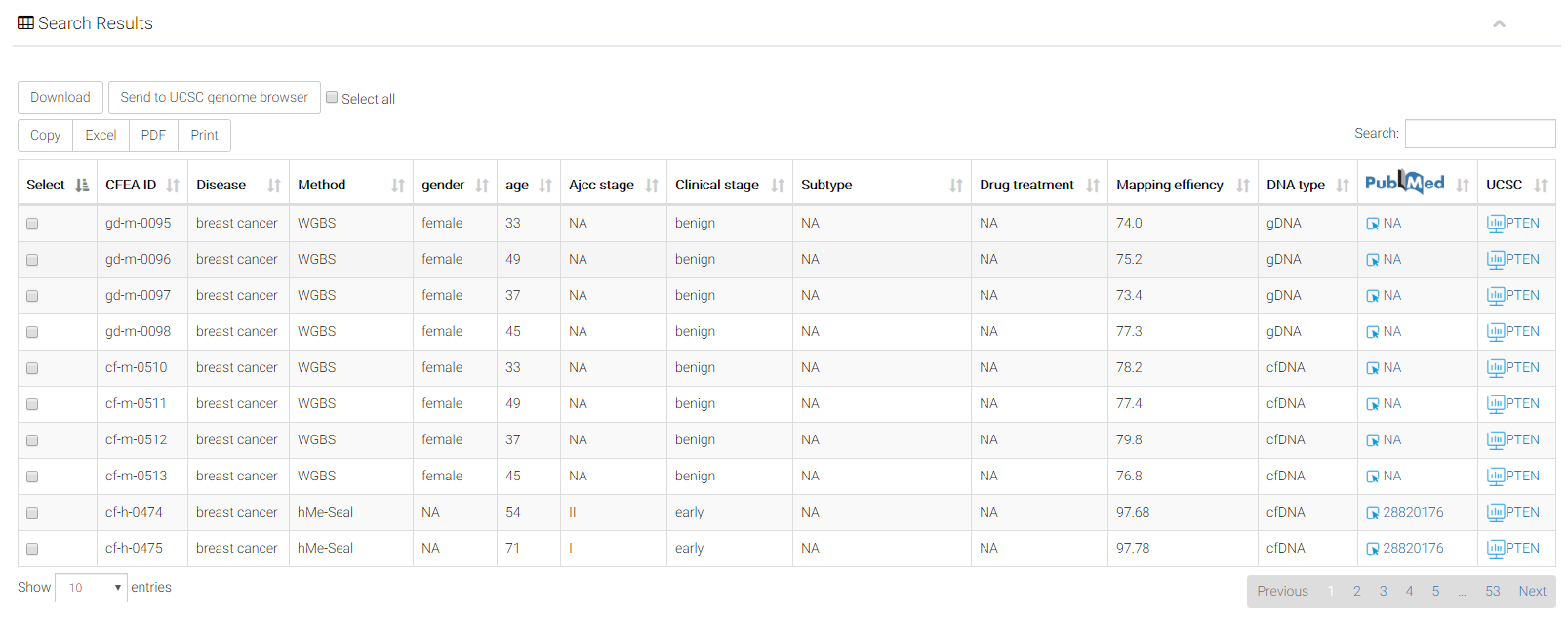
Similar to the search results of modification-specific browsers, the resulting table of cancer-stage browser has three more columns.
Ajcc stage: the original annotations of sample ajcc stages.
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AJCC_staging_system).
Clinical stage: clinical stage annotation for the patients with cancer.
Subtype: clinical subtype annotation for this malignant tumor.
In order to keep the data processed and stored in a consistent manner, CFEA developed benchmarking pipelines aiming at a broad range of experimental methods. We downloaded the raw sequence data from the public database and reanalyzed them with our CFEA pipeline. The source codes have been upload to the github website and could be used with non-commercial prupose (https://github.com/lemonsky123/CFEA-pipeline). We provide a step-by-step tutorial in the CFEA Pipeline page and github website to assist you to understand and use our pipeline to process your private data.
To download data in the database, select the menu "Download". CFEA provides two kinds of downloadable files in bed or bigwig format. The users can download all data including the human cell-free epigenome data classification by different detection methods.
